Overview
Before venturing into any advanced analysis of data using statistical, machine learning, and algorithmic techniques, it is essential to perform basic data exploration to study the basic characteristics of a dataset.
By studying it basic properties, we may find useful patterns (trend), connections, and relationships within data. This is usually called data exploration or exploratory data analysis (EDA).
The whole idea is to get better understanding of the dataset at hand. We want to know, whether our data is good or not.
Once we have good data, we can training our machine learning model and get accurate results.
Common Data Analysis
- descriptive statistic : summarizing, organizing, and presenting data meaningfully and concisely.
- catagorize by group
- data distribution
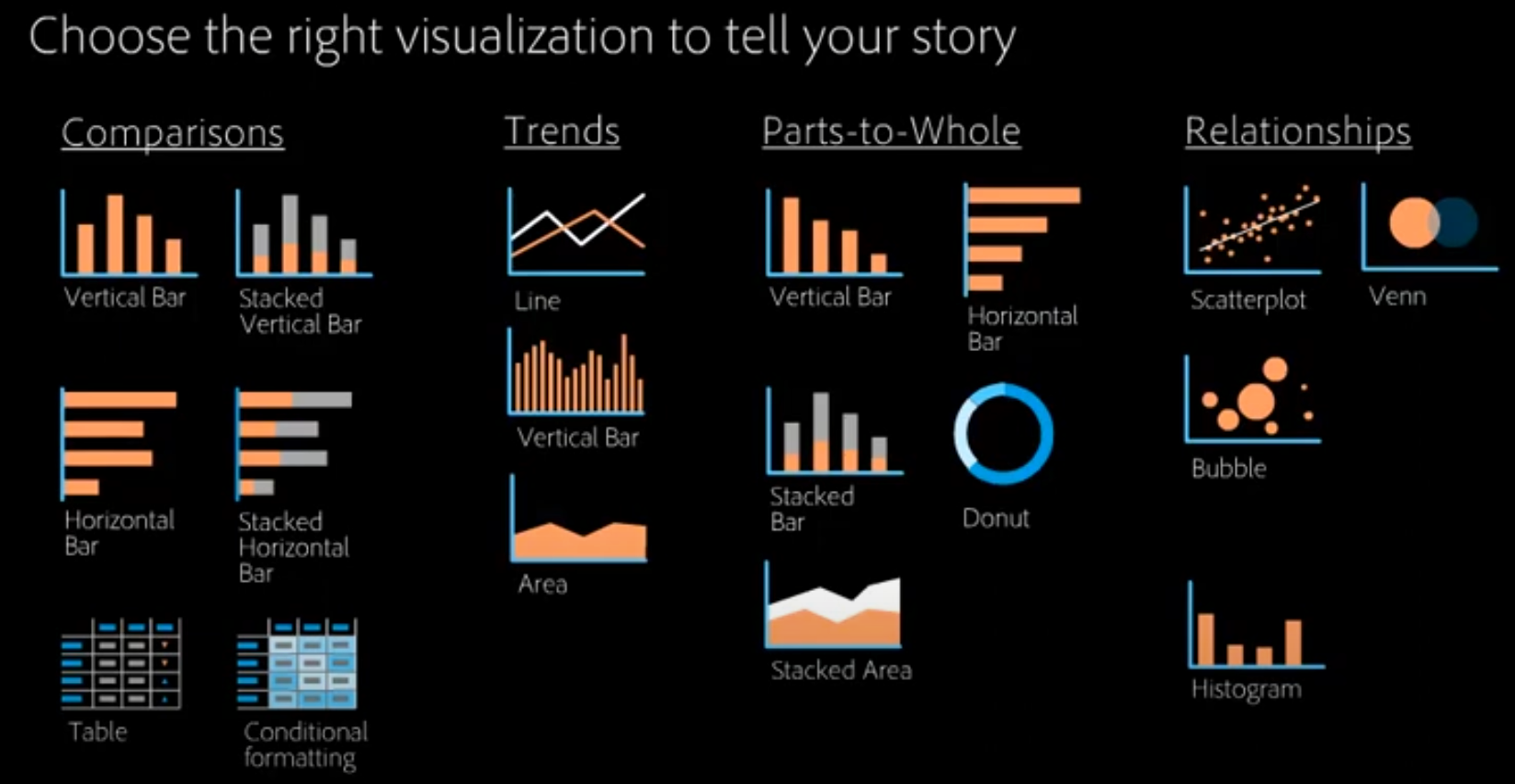
correlation analysis
- scatter plot \(\Longrightarrow\) two variables are plotted along two axes.
- pairplot \(\Longrightarrow\) pairwise relationships between variables within a dataset
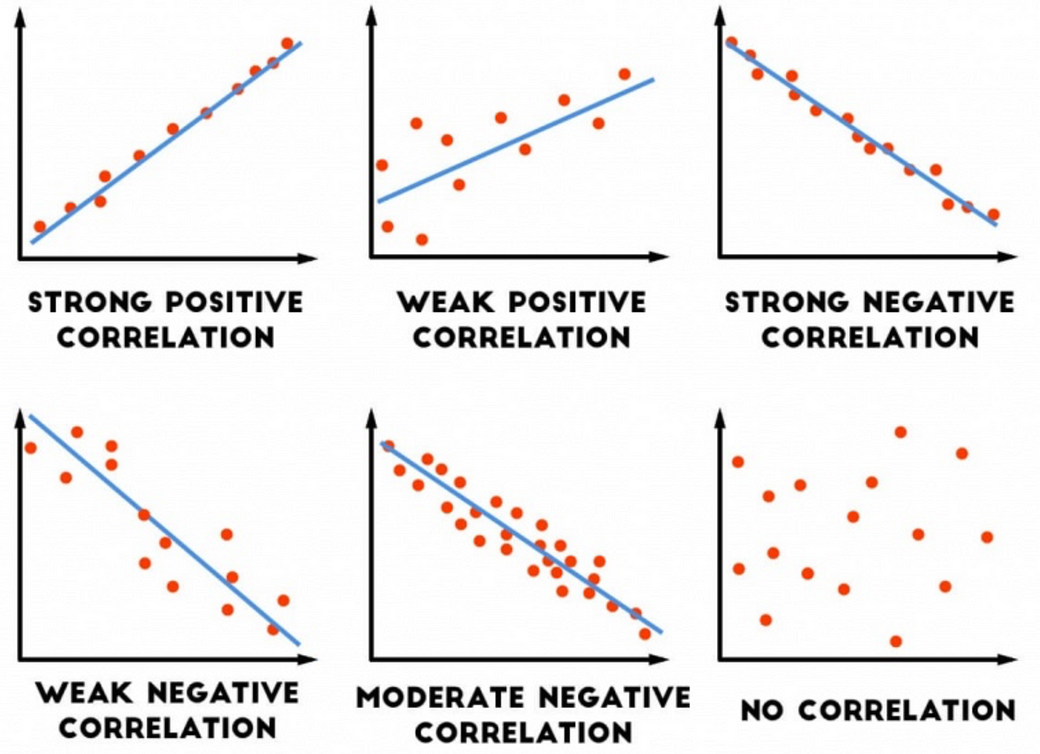
The closer the data points come to forming a straight line when plotted, the higher the correlation between the two variables, or the stronger the relationship.
If a relationship exists, the scatterplot indicates its direction and whether it is a linear or curved relationship. Relationships between variables can be described in many ways: positive or negative, strong or weak.
Common Data pre-processing
Data transformation
Many times in Machine Learning, we have to pre-process the data by “normalizing”, such as to set it to be in [0,1] (by scaling), or [-1,+1], scaling and centering, log or exponential, square root, etc. All these exercises do is only changing the scale and not the structure of the data. This is needed to assist computations and reduce computing errors, and not in any way doing anything beyond that. Furthermore, this will standardized numbers of various scales into same unique scale.
Missing-data imputation
Imputation is a technique used for replacing the missing data with some substitute value to retain most of the data/information of the dataset. These techniques are used because removing the data from the dataset every time is not feasible and can lead to a reduction in the size of the dataset to a large extend, which not only raises concerns for biasing the dataset but also leads to incorrect analysis.
Data Duplicate
To reduce model biased toward certain patterns in data, data duplicate should be remove.